Java多线程通信lock和wait
在Java多线程中有一对配合使用过的两个方法,来实现线程间通信的功能–lock和wait, 由于这个需要获得锁,所以必须结合synchronized一起使用。首先我们先看一个例子:
public class LockWait {
static volatile List<String> itemContainer = new ArrayList<>();
static Object obj = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread th1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("th1添加元素");
itemContainer.add(String.valueOf(i));
if (itemContainer.size() == 5) {
System.out.println("th1线程发出通知");
obj.notify();
}
}
}
});
Thread th2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("进入th2线程");
if (itemContainer.size() != 5) {
try {
System.out.println("th2线程开始等待");
obj.wait();
System.out.println("th2线程等待结束");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("th2线程结束");
}
}
});
th2.start();
th1.start();
}
}
输出结果如下:
进入th2线程
th2线程开始等待
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1线程发出通知
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th2线程等待结束
th2线程结束
具体运行逻辑如下:
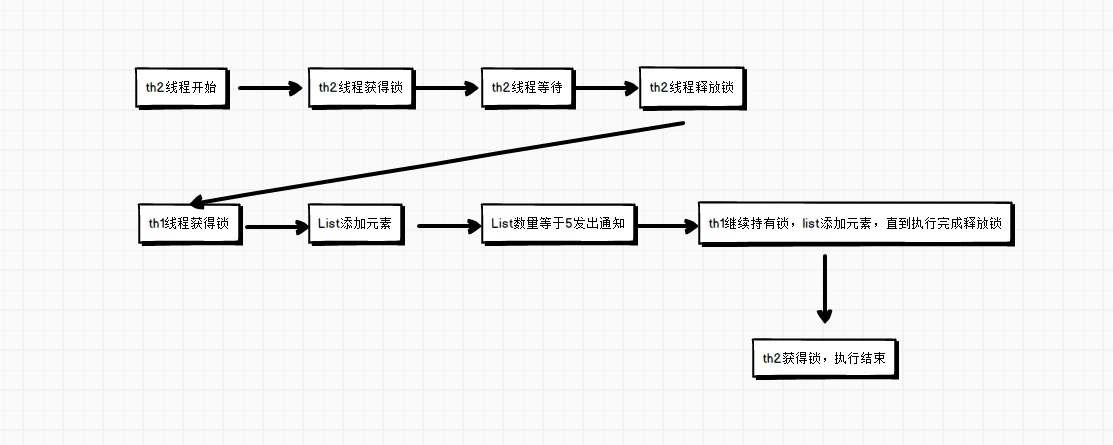
总结上面的运行结果,th2在wait的时候,th1可以持有锁。说明wait是释放锁,而notify不释放锁。
这样也就带来了一个弊端,无法实时的得到结果,就是说当List达到我们想要的结果的时候,th1线程一直还在持有锁,导致th2无法执行。
有没有更好办法呢?在Java中提供了一个CountDownLatch类:
public class CountDownLatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final List<String> itemContainer = new ArrayList<>();
final CountDownLatch countDownLanch = new CountDownLatch(1);
Thread th1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("th1添加元素");
itemContainer.add(String.valueOf(i));
if (itemContainer.size() == 5) {
System.out.println("th1线程发出通知");
countDownLanch.countDown();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread th2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("进入th2线程");
if (itemContainer.size() != 5) {
try {
System.out.println("th2线程开始等待");
countDownLanch.await();
System.out.println("th2线程等待结束");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("th2线程结束");
}
});
th2.start();
th1.start();
}
}
运行结果:
进入th2线程
th1添加元素
th2线程开始等待
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1线程发出通知
th1添加元素
th2线程等待结束
th1添加元素
th2线程结束
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
th1添加元素
Java多线程通信lock和wait
You need to set
install_url to use ShareThis. Please set it in _config.yml.