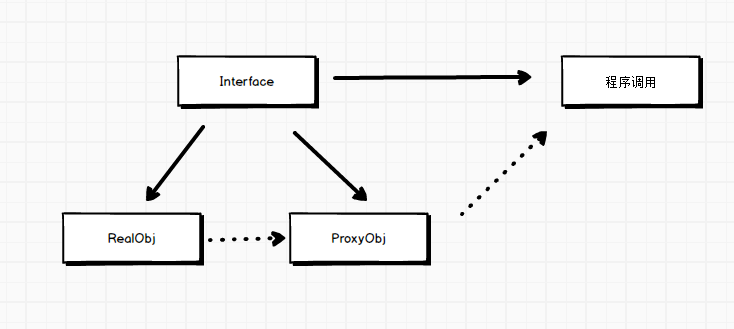
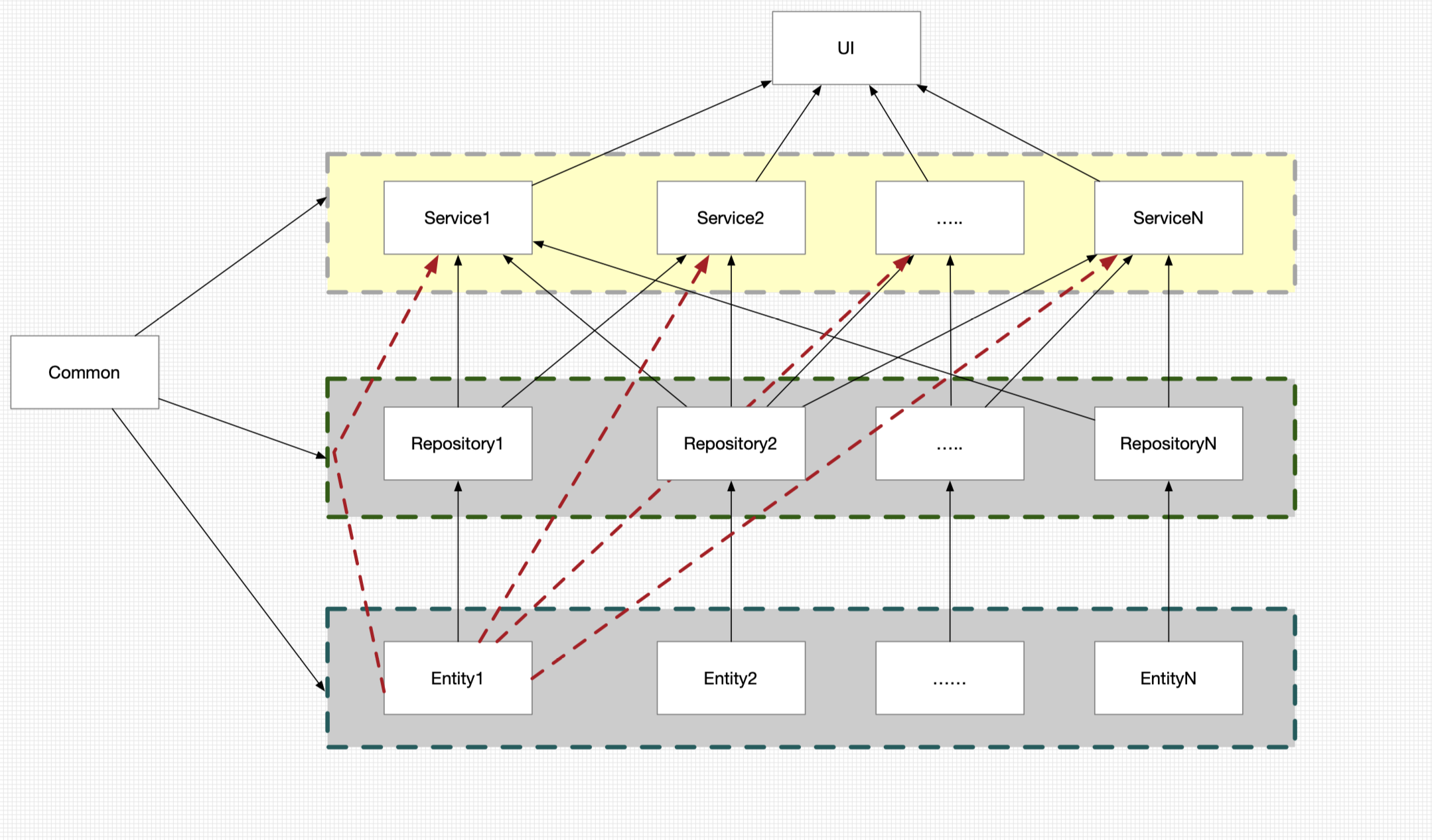
SpringMVC 概述
Spring 是目前比较流行的MVC框架,让POJO处理起来变的容易,也支持Rest的Url请求。采用松散的耦合可插拔的接口,比其它MVC接口更具有扩展性和灵活性
maven+spring+Idea 实现helloworld
下面就让我们用maven+Spring+Idea 实现一个 helloWorld的程序(至于环境的搭建可以直接到网上找个教程)
添加Maven项目
选择maven-archetype-webapp 这个项目类型
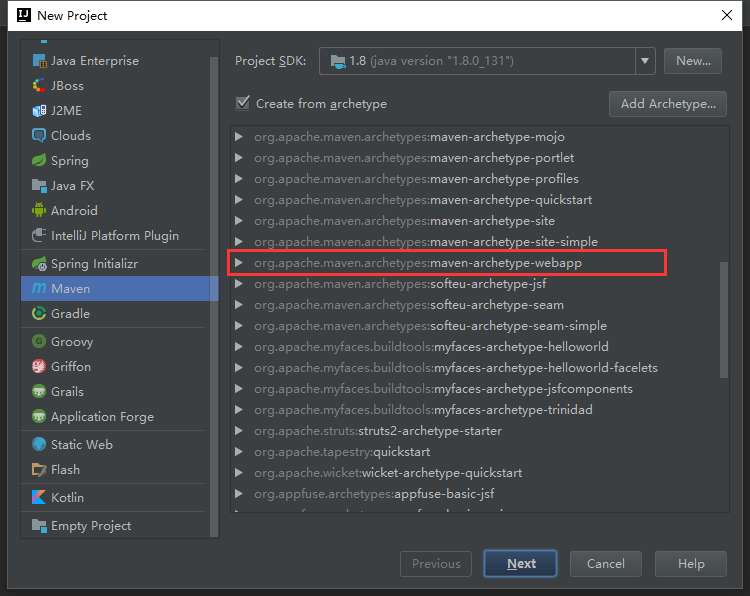
填写GroupId和ArtifactId后直接下一步直到创建完成
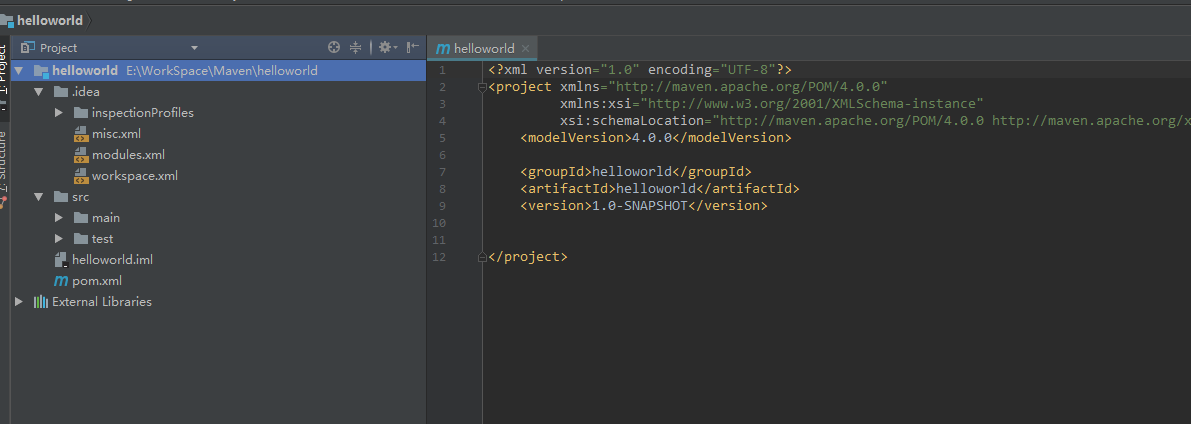
Maven生成的目录如下:
添加SpringMVC引用
对于MVC的使用,我们首先需要添加对SpringMVC的引用,使用Maven可以方便的实现对jar包的引用和版本的管理。
添加SpringMVC的引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
```
2. 添加对jsp的页面解析 jstl的引用
``` xml
<dependency>
<groupId>Javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>Javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>Javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
```
#### 添加SpringMVC配置
1. 添加Spring的配置文件,修改WEB-INF下面的web.config,添加如下内容
``` xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring-mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring-mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
Spring文件配置MVC,在resources文件夹下面添加对应的spring-mvc.xml,添加如下内容:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="redirectContextRelative" value="true"></property>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="Controller"></context:component-scan>
添加Controller和views
在main文件夹下添加Java目录,并标记为SourceRoot
添加Controller包,添加一个Controller代码:
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/Hello")
public String Hello(){
return "index";
}
}
添加views文件夹,新建一个index.jsp页面
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello World!</h2>
</body>
</html>
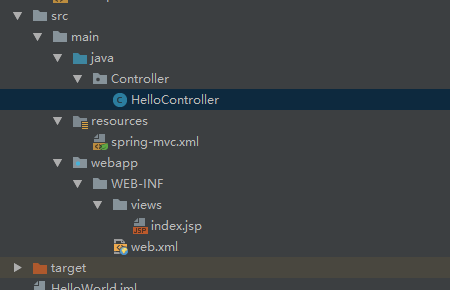
整体的项目的目录结构如下:
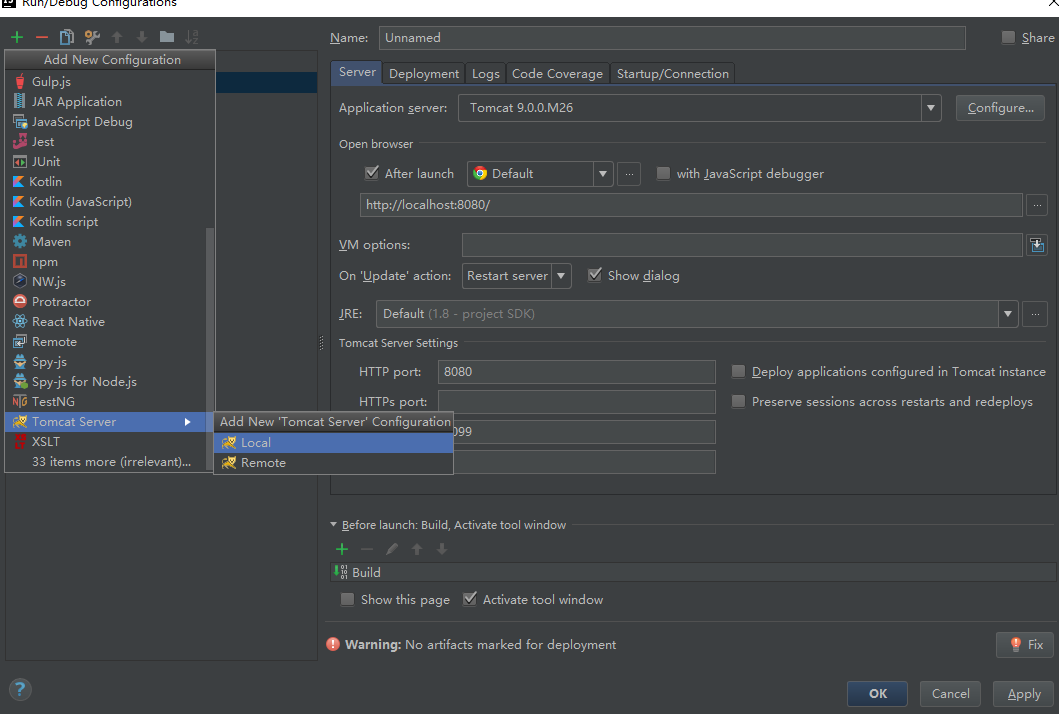
配置Tomcat
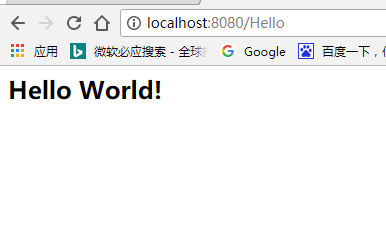
运行 Hello World
HelloWorld运行的过程
当我们在浏览器中发送一个Hello的请求,会被servlet-mapping所拦截,根据url的匹配格式跳转到指定的Controller,返回对应的值index值.
返回的值,会被指定的视图解析器解析为指定的物理的视图。对于 InternalResourceViewResolver 视图解析器,会做如下的的解析:
prefix+returnVal+suffix
这样的方式解析到指定的物理视图.
RequestMapping修饰方法
RequestMapping修饰方法
在上面的Demo中,我们用RequestMapping来修饰对应Controller中对应的方法,来说明当前的方法是这了响应Hello的请求。
RequestMapping的Value支持Ant通配符
在**@RequestMapping(“/Hello”)**映射中,我们让其匹配的是/Hello的url地址,RequestMapping也支持Ant通配符,具体的内容如下:
Ant 风格资源地址支持 3 种匹配符:
- ?:匹配文件名中的一个字符
- *:匹配文件名中的任意字符
- : 匹配多层路径
@RequestMapping 还支持 Ant 风格的 URL:
- /user/*/createUser: 匹配
- /user/aaa/createUser、/user/bbb/createUser 等 URL
- /user/**/createUser: 匹配 –
- /user/createUser、/user/aaa/bbb/createUser 等 URL
- /user/createUser??: 匹配 –
- /user/createUseraa、/user/createUserbb 等 URL
如果我们修改上述代码为:
@RequestMapping("/Hello/*/123")
public String Hello(){
return "index";
}
则使用:
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/Hello/myMvc/123
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/Hello/myMvc1231/123
….
都可以访问到Hello方法
RequestMapping修饰类
对于上面的Demo我们可以在HelloController上面添加RequestMapping来指定访问url的前缀的路径:
@RequestMapping("/SpringMVC")
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/Hello")
public String Hello(){
return "index";
}
}
如果Controller没有修复Request的修饰,则代表的是web的根目录。
RequestMapping的请求方式
RequestMapping可以指定请求的方式,demo如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "GetName",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String GetName(){
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "PostName",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String PostName(){
return "success";
}
修改Index的页面和添加一个success页面
<html>
<body>
<a href="/SpringMVC/GetName">GetName</a>
<br>
<a href="/SpringMVC/PostName">PostName</a>
</body>
</html>
Post页面的请求结果 :
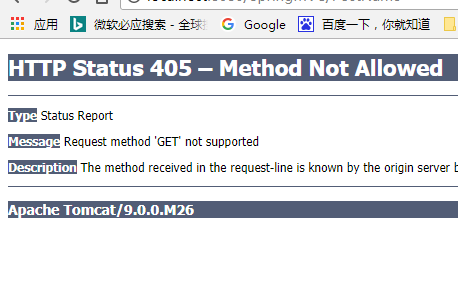
RequestMapping支持对参数和Header的定义,可以支持简单的表达式:
- param1: 表示请求必须包含名为 param1 的请求参数
- !param1: 表示请求不能包含名为 param1 的请求参数
- param1 != value1: 表示请求包含名为 param1 的请求参数,但其值
不能为 value1
- {“param1=value1”, “param2”}: 请求必须包含名为 param1 和param2
的两个请求参数,且 param1 参数的值必须为 value1
@RequestMapping(value ="TestParamsAndHeaders",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = {"userName","age!=10"},headers = {"Accept-Language:zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en;q=0.6"})
public String TestParamsAndHeaders(){
return "success";
}
<a href="/SpringMVC/TestParamsAndHeaders?userName=fuwei&age=11">TestParamsAndHeaders1</a><!--可以访问 -->
<br>
<a href="/SpringMVC/TestParamsAndHeaders?userName=fuwei&age=10">TestParamsAndHeaders2</a><!--不可以访问 -->
<br>
<a href="/SpringMVC/TestParamsAndHeaders?loginName=fuwei&age=10">TestParamsAndHeaders3</a><!--不可以访问 -->
上面的方法的映射要求是:必须要有userName参数,age!=10,且只接受zh-CN的语言的请求,如果修改上面的header中的accept的语言,则都无法请求。使用params和header可以更加精确的映射请求。
PathVariable注解
通过 @PathVariable 可以将 URL 中占位符参数绑定到控制器处理方法的入参中:URL 中的 {xxx} 占位符可以通过@PathVariable(“xxx”) 绑定到操作方法的入参中。这个能使得SpringMVC可以支持REST风格(关于Rest)。
@RequestMapping("/GetNameById/{id}")
public String GetNameById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
System.out.println(id);
return "success";
}
在浏览器中访问:
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/GetNameById/123123
可以在控制台打印出:123123
SpringMVC 获得请求参数方式
使用 @RequestParam
RequestParam来映射对应的参数,它具有3个属性:
value : 当前参数的值
require: 是否必须,默认是true
defalutValue: 默认值
@RequestMapping("/TestRequestParam")
public String TestRequestParam(@RequestParam(value = "userId",defaultValue = 0,required = true) int uid){
System.out.println(uid);
return "success";
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/TestRequestParam?userId=123 会在控制台打印出123
POJO 参数传递
对于表单提交来说,可能会有多字段,如果都使用@RequestParam则会比较麻烦。
针对这个问题我们可以使用POJO的方法进行传递 ,
Spring MVC 会按请求参数名和 POJO 属性名进行自动匹配,自动为该对象填充属性值。也可以使用级联属性。
如:userEx.dept.deptId、dept.address.tel 等
(其中的属性值与RequestParam 相同,不再赘述~~)
@RequestMapping("/TestRequestHeader")
public String TestRequestHeader(@RequestHeader(value = "Accept-Language") String lan){
System.out.println(lan);
return "success";
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/TestRequestHeader 打印出指定的语言版本:
zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en;q=0.6
@RequestMapping("/TestRequestCookie")
public String TestRequestCookie(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID") String sid){
System.out.println(sid);
return "success";
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/TestRequestCookie 打印出Cookie中的JSESSIONID。
@RequestMapping(value = "/TestPojo",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String TestPojo(User user){
ObjectMapper map=new ObjectMapper();
try {
System.out.println(map.writeValueAsString(user));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "success";
}
对应的html代码:
<form action="/SpringMVC/TestPojo" method="post">
<input name="UserName"/><br><br>
<input name="UserMail"/><br><br>
<input name="Dept.DeptId"/><br><br>
<input name="Dept.Addr.Povince"/><br><br>
<input name="Dept.Addr.City"/><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
填写信息打,在后台印出:
{
"userName": "username",
"dept": {
"addr": {
"povince": "shanghai",
"city": "changning"
},
"deptId": 10
},
"userMail": "userMail"
}
Servlet原生的API参数
SpringMVC支持以下类型Servlet参数 :
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpSession
- Java.security.Principal
- Locale
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Reader
- Writer
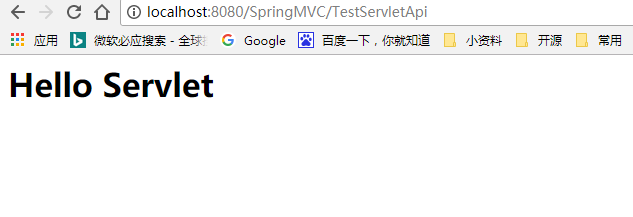
@RequestMapping(value = "/TestServletApi")
public String TestServletApi(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
try {
System.out.println("TestServletApi HttpServletRequest:"+request.getRequestURL());
response.getWriter().write("<h1>Hello Servlet<h1/>");
response.getWriter().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "success";
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/TestServletApi
控制台打印: http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/TestServletApi
浏览器返回:Hello Servlet