在Java中对于变量的访问分为3种,分别为强引用,软引用和弱引用 . 在这篇博客中可以认识到三种引用的类型的特点和使用场景。 首先通过一段代码来认识三者的区别:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package com.pay.utils;
import Java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import Java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
public class WeakRefDemo {
public static void main(String... args) {
Object objA = new Object();
Object objB = new Object();
Object objC = new Object();
Object strongA = objA;
SoftReference<Object> softB = new SoftReference<>(objB);
WeakReference<Object> weakC = new WeakReference<>(objC);
objA = null;
objB = null;
objC = null;
System.out.println("GC前各变量的值:");
System.out.println(String.format("strongA = %s, softB = %s, weakC = %s", strongA, softB.get(), weakC.get()));
System.out.println("执行GC");
System.gc();
System.out.println("GC之后:");
System.out.println(String.format("strongA = %s, softB = %s, weakC = %s", strongA, softB.get(), weakC.get()));
}
}
|
打印结果如下:
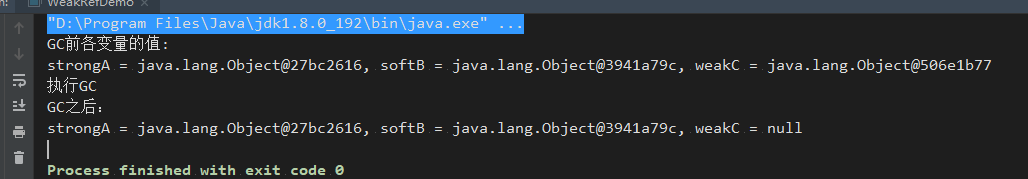
可看到三个类型的引用在GC之后的表现:
强类型: 是常用的引用类型,如果变量正在被引用,在内存不足的情况下,jvm抛出OutofMemory也不会回收。软类型: 在内存不足的情况下才会被回收,比较适合作为缓存使用。弱引用: 等同于没有引用,在GC回收的时候,如果发现都是弱引用,则会判断为没有引用,可以直接被GC垃圾回收。
