MINST数据库是由是一个手写数字的数据集,官方网址:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ 。
> MNIST 数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). 训练集 (training set) 由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成, 其中 50% 是高中学生, 50% 来自人口普查局 (the Census Bureau) 的工作人员. 测试集(test set) 也是同样比例的手写数字数据.
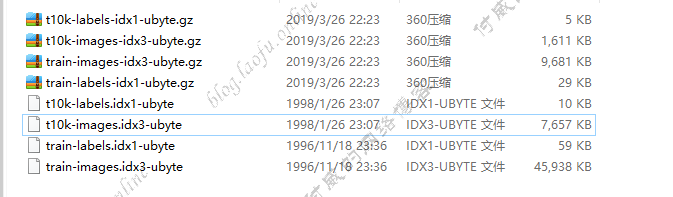
MINST数据总共有4个包,解压出来的数据如下:
train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz,train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz:提供了60000张,28*28像素的黑底白字图片用来训练t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz,t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz:提供了10000张,28*28像素的黑底白字图片用来测试
mnist提供的图片有784(28*28)个像素点,把每个像素点的值,组织成一个一维的数组,作为输入参数。形式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.386 0.379 0....... 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. ] ``` 图片的标签以一维数组给出,每个元素代表出现的概率,形式如下: `[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. ]` 代表数字6 `tensorflow`官方支持数据集的读取,使用代码如下: ``` python # coding:utf-8 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data minst=input_data.read_data_sets('./data/',one_hot=True) #打印数据数量 print( "train data size:",minst.train.num_examples) print( "validation data size:",minst.validation.num_examples) print( "test data size:",minst.test.num_examples) #打印数据 print(minst.train.labels[0]) print(minst.train.images[0]) #打印前200行数据 BATCH_SIZE=200 xs,ys=minst.train.next_batch(BATCH_SIZE) print("xs shape:",xs.shape) print("ys shape:",ys.shape) ``` 输出到控制台结果: ``` cte train data size: 55000 validation data size: 5000 test data size: 10000 [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0.....0. 0.3529412 0.5411765 0.9215687 0.9215687 0.9215687 0.9215687 0.9215687 0.9215687 0.9843138 0.9843138 0.9725491 0.9960785 0.9607844 0.9215687 0.74509805 0.08235294 0. 0. 0.....] xs: [[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] ... [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]] xs shape: (200, 784) ys: [[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 1. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] ... [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.] [1. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]] ys shape: (200, 10)
既然是图片数据,我们就能把他们都还原过去,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import numpy as npimport structfrom PIL import Imageimport osdata_file = 'train-images-idx3-ubyte' data_file_size = 47040016 data_file_size = str (data_file_size - 16 ) + 'B' data_buf = open (data_file, 'rb' ).read() magic, numImages, numRows, numColumns = struct.unpack_from( '>IIII' , data_buf, 0 ) datas = struct.unpack_from( '>' + data_file_size, data_buf, struct.calcsize('>IIII' )) datas = np.array(datas).astype(np.uint8).reshape( numImages, 1 , numRows, numColumns) label_file = 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte' label_file_size = 60008 label_file_size = str (label_file_size - 8 ) + 'B' label_buf = open (label_file, 'rb' ).read() magic, numLabels = struct.unpack_from('>II' , label_buf, 0 ) labels = struct.unpack_from( '>' + label_file_size, label_buf, struct.calcsize('>II' )) labels = np.array(labels).astype(np.int64) datas_root = './pic/' if not os.path.exists(datas_root): os.mkdir(datas_root) for i in range (10 ): file_name = datas_root + os.sep + str (i) if not os.path.exists(file_name): os.mkdir(file_name) for ii in range (numLabels): img = Image.fromarray(datas[ii, 0 , 0 :28 , 0 :28 ]) label = labels[ii] file_name = datas_root + os.sep + str (label) + os.sep + \ str (ii).zfill(5 ) + '.png' img.save(file_name)
 {:height=”600px” width=”600px”}
{:height=”600px” width=”600px”}