Java中实现顺序IO
顺序IO和随机IO
对于磁盘的读写分为两种模式,顺序IO和随机IO。 随机IO存在一个寻址的过程,所以效率比较低。而顺序IO,相当于有一个物理索引,在读取的时候不需要寻找地址,效率很高。
网上盗了一个图(侵权删)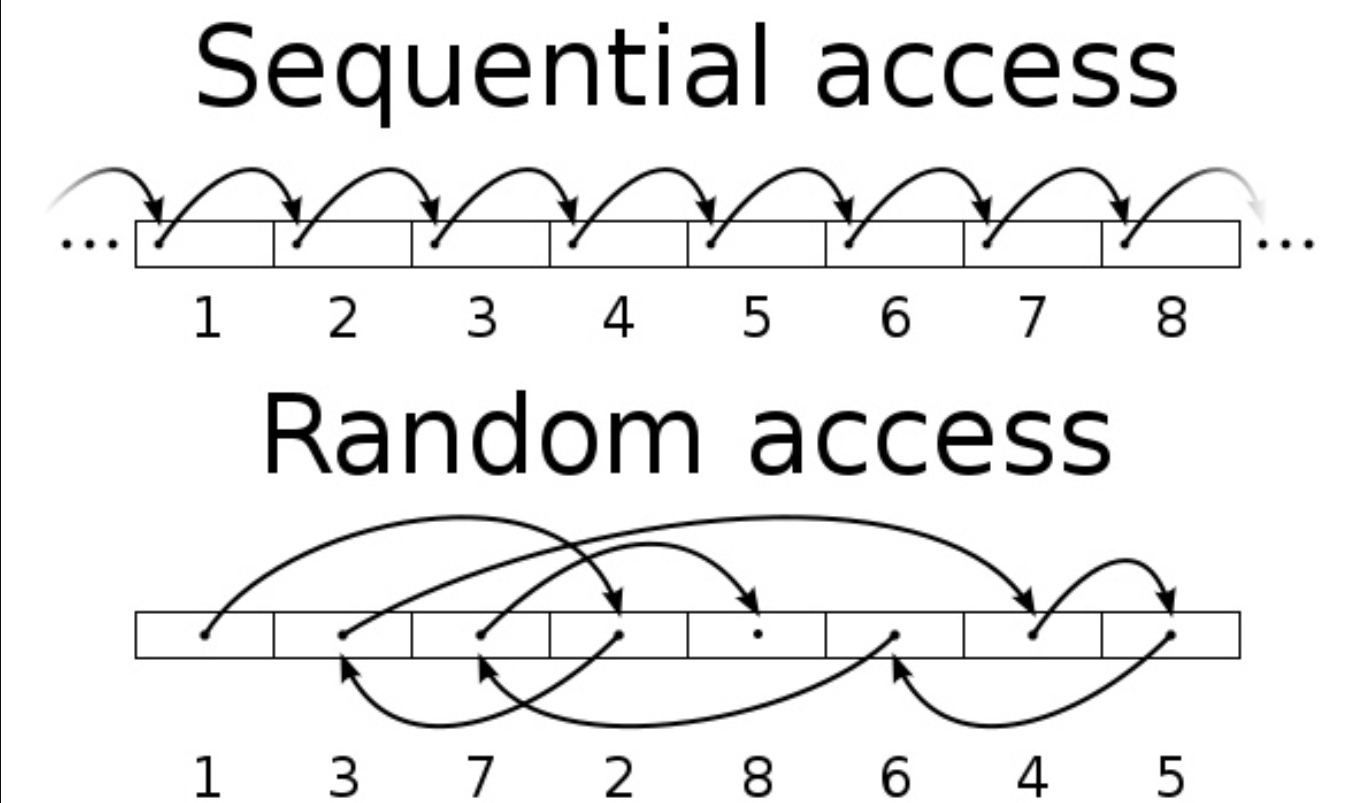
Java中的随机读写
在Java中读写文件的方式有很多种,先总结以下3种方法:
FileWriter和FileReader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public static void fileWrite(String filePath, String content) {
File file = new File(filePath);
//创建FileWriter对象
FileWriter writer = null;
try {
//如果文件不存在,创建文件
if (!file.exists())
file.createNewFile();
writer = new FileWriter(file);
writer.write(content);//写入内容
writer.flush();
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void fileRead(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
try {
//创建FileReader对象,读取文件中的内容
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
char[] ch = new char[1];
while (reader.read(ch) != -1) {
System.out.print(ch);
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter与
FileWriter和FileReader代码的写法一致,Buffer也多了一个读取一行字符的操作。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36public class BuffredRWHelper {
public static void fileWrite(String filePath, String content) {
File file = new File(filePath);
//创建FileWriter对象
BufferedWriter writer = null;
try {
//如果文件不存在,创建文件
if (!file.exists())
file.createNewFile();
writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
writer.write(content);//写入内容
writer.flush();
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void fileRead(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
try {
//创建FileReader对象,读取文件中的内容
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.print(line);
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
使用Stream的形式是最原始的方式,以字节数组为中间的中转缓解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41public static void fileWrite(String filePath, String content) {
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
boolean isCreate = file.createNewFile();//创建文件
if (isCreate) {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);//形参里面可追加true参数,表示在原有文件末尾追加信息
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}else {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file,true);//表示在原有文件末尾追加信息
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void fileRead(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
try {
//创建FileInputStream对象,读取文件内容
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
while (fis.read(bys, 0, bys.length) != -1) {
//将字节数组转换为字符串
System.out.print(new String(bys, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Java中的顺序读写
上面的对文件的读写都是随机读写,如果用来写比较小的日志文件还能满足要求,如果用来操作一个文件的读写,那可能带来很大的性能消耗。
顺序IO的读写在中间件使用的很频繁,尤其是在队列中。几乎所有的队列(kafka,qmq等使用文件存储消息)都采用了顺序IO读写。
与随机读写不同的是,顺序读写是优先分配一块文件空间,然后后续内容追加到对应空间内。
在使用顺序IO进行文件读写时候,需要知道上次写入的地方,所以需要维护一个索引或者轮询获得一个没有写入位置。
1 | public static long fileWrite(String filePath, String content, int index) { |
这种读写的方式是采用的mmap的一种机制,什么是mmap呢?
mmap是一种内存映射文件的方法,将一个问文件或者其他的对象映射进内存,文件被映射到多个页上。文件的读写也是直接操作内存,真正落地的成文件依赖操作系统的刷盘的机制,当然系统也提供接口来强制刷盘。
由于顺序IO不需要寻址和mmap的机制,所以顺序IO的读写基本上与内存的读写效率基本上一致。