容器的种类 为什么要使用容器? 因为数组不能够满足日常的开发需求,数组有以下弊端:
长度难以扩充
数据的类型必须相同
数组无法获得有多少个真实的数据,只能获得数组的长度。
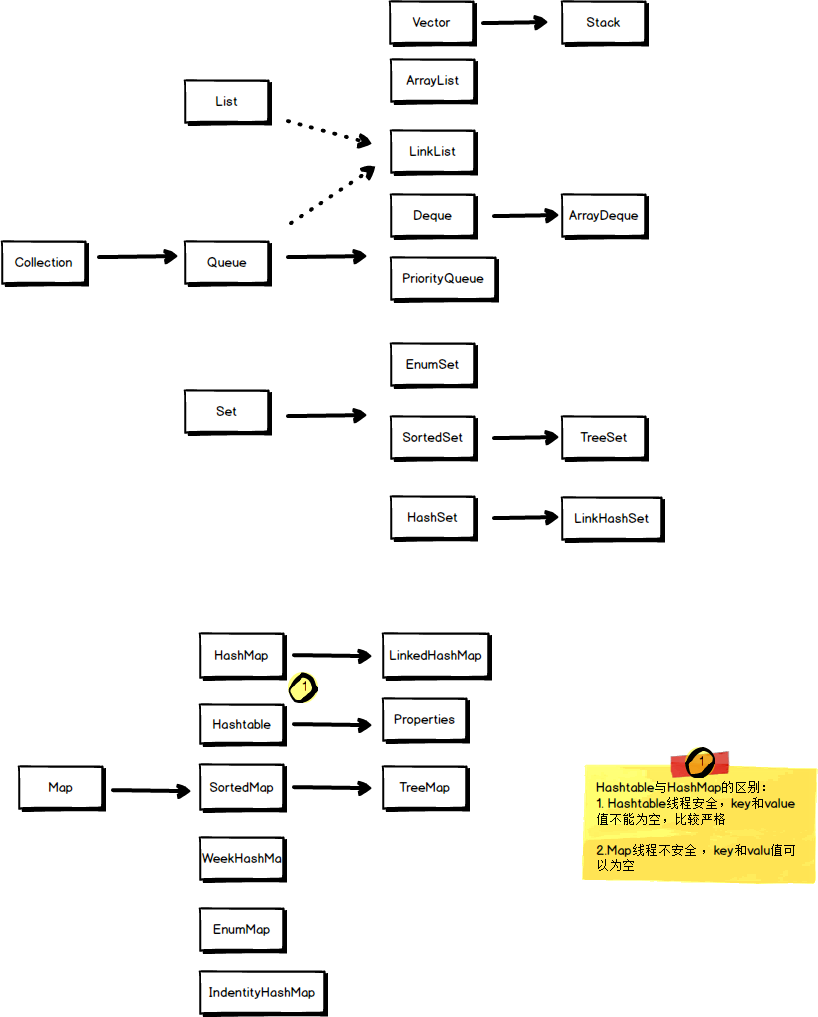
在Java中有常用的三种类型的容器,分别是List 、Map、Set,基于这个三个基本的类型,派生出很多其它的类型,具体关系如下:
三者的区别:
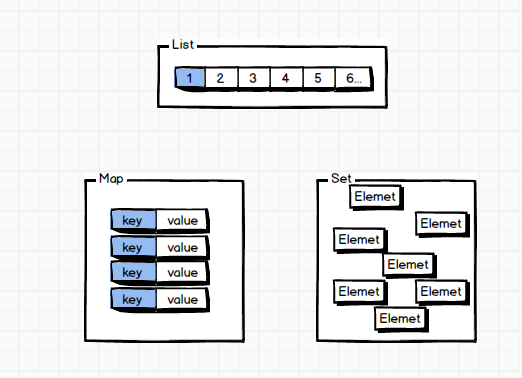
Set(集):与list都是有Collection类的派生出来, 分辨各个元素的标识是HashCode,所以元素不能有重复
List(列表):是一个有序的列表,元素如果有重复,也会一一列出来。
Map(映射): Map是我们常说的键值对,有key和Value两个元素
使用方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Test public void ContainerTest () { String string[] = {"i" , "am" , "am" , "xiao" , "ming" }; List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); for (String s : string) { list.add(s); } System.out.println("List执行结果:" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); } Set<String> set = new HashSet <String>(); for (String s : string) { set.add(s); } Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); System.out.println("===================" ); System.out.println("Set 执行结果:" ); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } ``` 运行结果: ```cte List执行结果: i am am xiao ming =================== Set 执行结果: ming xiao i am
三者的区别可以表示如下图:
各个容器的说明和使用 List ArrayList ArrayList是List一个派生类,非线安全,是基于Object数组实现的可动态扩展的容器,在调用Add的时候会判断当前的长度是否已经超过了Size.对应的Add方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
LinkList LinkList与ArrayList区别是LinkList 是基于链表的结构设计 ,插入和删除的性能要高于ArrayList,查询的效率低于LinkList,使用方法基本一致,也是非线安全,下面看下性能测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 @Test public void ListAdd () { System.out.println("ArrayList ADD耗时:" + AddList(new ArrayList ())); System.out.println("LinkedList ADD耗时:" + AddList(new LinkedList ())); final int N = 50000 ; Integer vals[] = new Integer [N]; Random r = new Random (); for (int i = 0 , currval = 0 ; i < N; i++) { currval += r.nextInt(100 ) + 1 ; vals[i] = new Integer (currval); } List lst = Arrays.asList(vals); System.out.println("ArrayList Search耗时:" + SearchList(new ArrayList (lst))); System.out.println("LinkedList Search耗时:" + SearchList(new LinkedList (lst))); } long AddList (List list) { final int N = 50000 ; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object o = new Object (); for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) list.add(0 , o); return System.currentTimeMillis() - start; } long SearchList (List lst) { final int N = 50000 ; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { int index = Collections.binarySearch(lst, lst.get(i)); if (index != i) System.out.println("***错误***" ); } return System.currentTimeMillis() - start; } ``` 运行结果: ``` cte ArrayList ADD耗时:396 LinkedList ADD耗时:9 ArrayList Search耗时:20 LinkedList Search耗时:8330
Vector 比arraylist多了个同步化机制(线程安全),用法相同,但效率比较低,不建议使用。
Map HashMap 和 HashTable 二者在使用上功能差不多,区别是HashMap是线程不安全,允许多线程去同时访问,允许插入空值。 而HashTable是相反的,对于HapMap的使用,可以参考下面代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Map map=new HashMap (); map.put("key" ,"abc" ); map.put("key1" ,"abc1" ); map.put("key2" ,"abc2" ); System.out.println(map.get("key" )); map.remove("key" ); System.out.println(map.values()); System.out.println(map.keySet()); System.out.println(map.entrySet());
运行结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 abc [abc1, abc2] [key1, key2] [key1=abc1, key2=abc2]
TreeMap 是一个有顺序的HaspMap
手工实现容器ArrayList 根据上面的分析,我们可以手工实现一个ArrayList 代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class MyArrayList { private Object[] _arr; private int _size; public MyArrayList () { _arr = new Object [10 ]; this ._size = 0 ; } public void Add (Object obj) { if (this ._size >= this ._arr.length) { Object[] newArray = new Object [2 * this ._size + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ._size; i++) { newArray[i] = this ._arr[i]; } this ._arr = newArray; this ._arr[this ._size] = obj; this ._size++; } else { this ._arr[this ._size] = obj; this ._size++; } } public int Size () { return this ._size; } public Object get (int index) { if (index > this ._size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("索引超出界限" ); } return this ._arr[index]; } }
使用方法:
@Test
public void PrintMyArr(){
MyArrayList list=new MyArrayList();
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++){
list.Add(i);
}
System.out.println(list.Size());
System.out.println(list.get(503));
System.out.println(list);
}